As our first unit in History 12, we did an in depth study on political Ideologies and the dynamic of the political spectrum. Personally, as somebody who loves to learn about the brutal wars of the 20th century, the tense nuclear arms race of the Cold War, and other modern conflicts in history, originally I was not too jazzed to be learning about the political spectrum as our very first taste of History 12. I mean, how boring, right..? Wrong! Through writing this blog post months after completing the unit, I now realize how crucial it is to have a thorough understanding of the political spectrum, and the different political Ideologies, as it has connected and related to almost every topic that we’ve learned so far this year.
From previous years in school I knew that there are right wing and left wing principles when it comes to making decisions in government, and most people stand somewhere in the middle when it comes to forming a political opinion.

Some party’s, such as the Canadian Conservatives and the US Republicans, appeal to those that have more of a traditional right wing stance when it comes to making laws and forming government policies. However, other party’s, such as the Liberals in Canada and the Democrats in the United States, appeal to those that have more of a left wing point of view. But wait a minute, what even is this so called thing known as the political spectrum? And how do you differentiate the key morals and values of someone who has a far right stance versus someone who has a far left stance?
It’s quite complicated to explain, but, to simplify it as much as I can, someone who is far right wing has opposite morals, values, and ideals as someone who is far left wing. Historically, right wing political parties promote established values and policies, and work hard in conserving and following an established framework/constitution. In contrast, left wing political parties promote change, radicalism, reform and constitutional development. Someone who is left wing often considers established values and policies unworthy of conserving. To put that into context, communism and socialism are usually regarded internationally as being on the left, where as conservatism and capitalism are on the right.
In order to further describe and differentiate the difference between right and left wing politics, I created this detailed chart below, using several different resources that I found online, to showcase the difference in political opinions on certain societal issues.
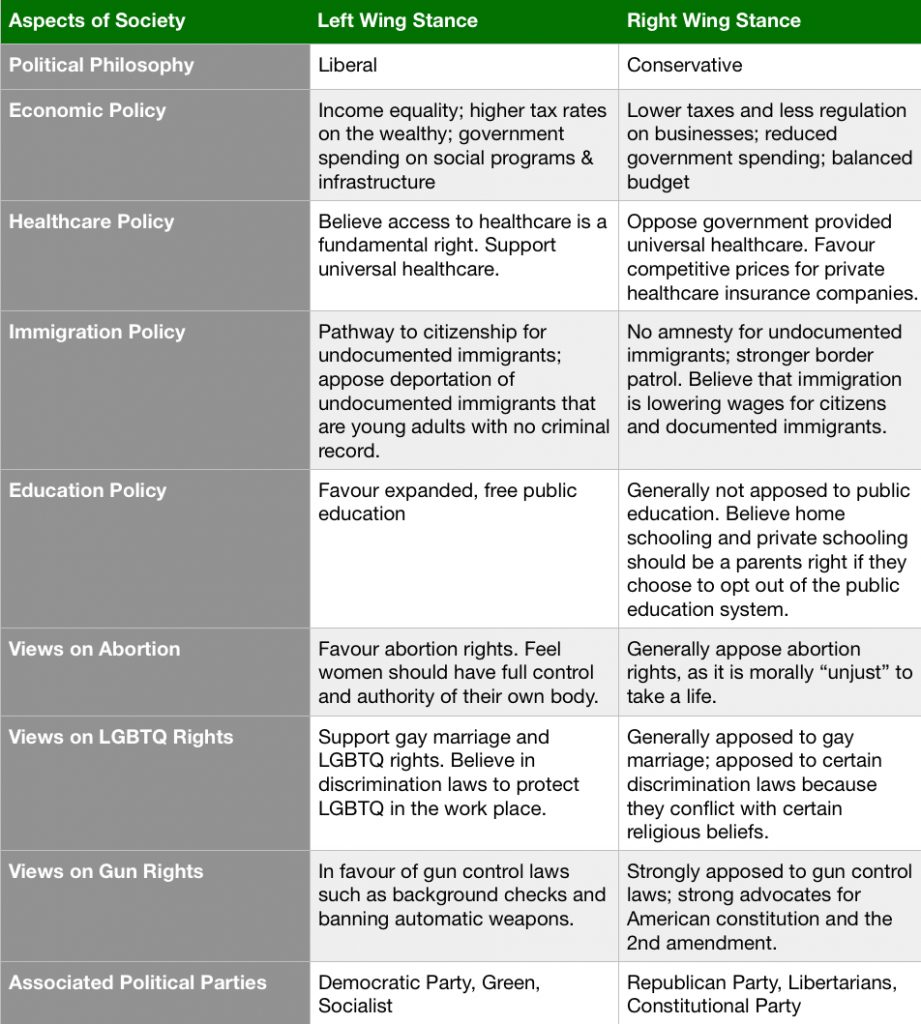
Chart analysis of Left – Right wing politics.
Along with learning the right wing – left wing political spectrum in class, we also learned about every single type of political ideology that exists around the world today and in the past. The notes I took on each individual ideology are imbedded below, as its way to much to summarize in my own words.
Insert ideology notes





Through learning about all the different political ideologies, I was able to immediately gain a better understanding of what’s happening around the world, and why ideological wars have been so common throughout history. An ideology is a set of political ideas that embody or articulate class of social/economic interests, and, when’s there’s such opposite ends to the political spectrum, it’s easy to see how ideological wars can stem purely from having opposite beliefs, that directly contradict everything you stand for, to someone else who may be your next door neighbour or best friend.
As a historical connection, some may argue that the Cold War stemmed purely from the nuclear arms/space race of the two biggest world super powers to ever exist, the US and the USSR. However, in reality, the Cold War was an ideological fight between the democratic, free West and the major communist powers in the east to see which set of political ideals would prevail. Nevertheless, after learning about the 13 different ideologies it’s easy for one to understand that there’s actually a lot more to the complicated world political dynamic than just communism and capitalism, and the common right wing – left wing political spectrum.
Throughout the coarse of history, it has become increasingly clear, through conducting studies and learning about the complicated ideological systems of the world, that the generic left wing – right wing political spectrum is very insufficient for describing the existing variation in political beliefs. The current political spectrum, which scientists have derived from years of research, often includes other axis to articulate social/political interests, as well as political opinion, to articulate where someone may stand within world politics. Often in popular political spectrum visuals, the 4 axis are split between social cultural issues and economic issues, each scaling from some form of individualism (or government for the freedom of the individual) to some form of communism (or government for the welfare of the community).
Below is a political spectrum visual, along with a visual that showcases famous historical indicuals theatre examples of being far left or right, and finally a visual of where I stand on the spectrum.

A general, informative visual of the Political Spectrum.

Famous names on the political spectrum, and where they fit in along the axis.

Where I stand on the political spectrum.
As a baseline assignment for this unit, I completed the detailed ideology notes imbedded above. Through completing such detailed, formatted notes I was able to retain the information taught in class much better than if I was just listening. Also, going into post secondary next year it’s really important to know how to take proper notes, a skill you’re never really taught in high school, and throughout this political Ideologies unit I obtained that skill.